Solar Energy
"To truly transform our economy, protect our security and save our planet from the ravages of climate change, we need to ultimately make clean, renewable energy the profitable kind of energy." - Barack Obama, 2009
What is it?

There are various forms of energy. They include thermal, electromagnetic, chemical, electrical, electrochemical, sound, potential, and kinetic energy. Solar energy is energy from the sun and arrives in two forms: thermal (heat) energy and electromagnetic (light) energy. Solar energy is a clean and renewable alternative energy source.
Why should we use it?
Solar energy is completely limitless and free! It can be used worldwide, no matter the climate (even in rainy or snowy areas, solar panels and other devices will be able to transmit the sun's rays as energy). Since it is a renewable resource, the use of solar energy has nearly no environmental impact, thus reducing our carbon footprint.
History of Solar Energy700 B.C.--Magnifying glass is used to create fire by concentrating the sun's rays.
200 B.C.--Archimedes, a Greek scientist, used solar reflectors made of bronze to set Roman ships on fire. 1767--Horace de Saussure, a Swiss scientist, created the first solar collector which was used to cook food. 1839--Edmond Becquerel, a French scientist, discovers the photovoltaic effect (generation of electricity increases in the presence of light). 1876-- William Grylls Adams and Richard Evans Day find that when put in light, the element selenium generates electricity. 1883--Charles Fritts, an American inventor, makes the first solar cells from selenium wafers. 1891--Clarence Kemp, an inventor, patents the first solar water heater. 1905--Albert Einstein publishes a paper on the theory of relativity and the photoelectric effect (electromagnetic radiation is composed of photons which hit electrons on metal and emit electrons). 1954--Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller and Gerald Pearson create the first silicon photovoltaic cell, thus beginning PV technology. 1964--NASA launches Nimbus, the first solar powered satellite. 1977--US Department of Energy creates the Solar Energy Research Institute. 1981--The Solar Challenger, the first solar powered aircraft is made. 1982--The Quiet Achiever, the first solar powered car is made. 1991--President Bush designates the Solar Energy Research Institute as the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. 1998--The first flexible solar panels are made as a result of amorphous silicon which leads to the creation of BIPV (Building Integrated Photovoltaic) roof shingles 2000--The largest solar array in space is started on the International Space Station. It has about 65,600 solar cells. |
How does it work? |
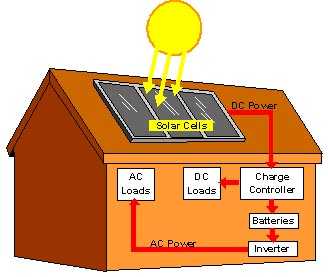
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It can, however, change from one form to another. We can capture solar energy and convert it into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) solar systems. To do so, solar panels consisting of layers of silicon wafers absorb light particles, or photons, when struck by sunlight. The impact causes the photons to release their charge, generating electricity. The electric current is collected in the charge controller, a piece of equipment which regulates battery voltage. It is then either stored in batteries in the direct current (DC) form of electrical energy or transferred to an inverter which converts the DC into the alternating current (AC) form of electrical energy. Loads (such as motors), which may require either DC or AC power formats, are then placed at the end of the system which receive power from the electricity generated by the PV system.
|
|
|
|
Traditional Energy vs. Solar Energy
Environmental Impact
Traditional:
|
Solar:
|


The solar panel used in calculation refers to a 1,000 watt photovoltaic cell.
Cool Applications of Solar Energy
MS Tûranor PlanetSolarThis yacht is the largest solar ship in the world. Its deck is covered with 537 square meters of solar panels that generate enough power to charge six blocks of lithium-ion batteries. Not only is the MS. Tûranor PlanetSolar the first boat to circumnavigate the world solely using solar energy (completing the journey in 1 year, 7 months, and 7 days), but it also holds the record for the fastest crossing of the Atlantic Ocean by a solar-powered craft (taking 26 day, 19 hours, and 10 minutes), the fastest crossing of the South China Sea by a solar-powered craft (taking 4 days, 23 hours, and 45 minutes), and longest distance ever traveled by a solar-powered craft (a total of 60,006 kilometers or 37,286 miles)!
Click on the link below for more information and watch the video (see right)! http://www.planetsolar.org/! BigBelly Solar Trash CompactorsThese unique trash compactors are often used in large cities and utilize solar energy to reduce the influence of trash. By compacting the trash, less pickups are made thus saving gas and decreasing the amount of greenhouse gas emissions. First created in 2003 in Massachusetts, the BigBelly Solar has been very successful with sales in all 50 states and 30 countries. There are approximately 1,000 BigBelly units in Philadelphia alone! Besides cities, these trash compactors are used in colleges, universities, parks, public areas, healthcare areas and more. As they continue to improve and expand, trash pick-up and recycling habits have advanced.
Click on the link below to learn more! Benefits of sustainability! |
National Stadium (Kaohsiung, Taiwan)The stadium to the left, which hosted the 2009 World Games, is the largest stadium in the world that provides power through solar energy. Its roof is covered in 8,844 solar panels that have the ability to produce one million kilowatt-hours of electricity. Each year, the stadium produces 1.1 million kilowatt-hours of power and sends its excess power back to the grid through the Taiwan Power Company. In addition to solar energy, the National Stadium of Sports Affairs Council also promotes bio-resource conservation through biodiversity and urban greenery.
Click the links below to learn more! Stadium's solar energy application! Stadium's bio-resource conservation efforts! |
2014 Solar Energy Lesson
Don't need to turn in the worksheet? Please let us know what you have learned digitally by taking the survey version below!